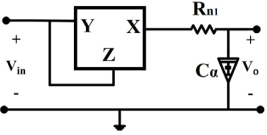
The two-port network is one of the important concepts in electric circuit analysis. The basic idea is to treat some connected components of a circuit as a separate entity and deal with it as a black box. This black-box / network has four terminals that are arranged as two ports (input and output ports). The purpose of two-port network is to extract the relationships between the input/output currents and voltages as a matrix to characterize and analyze any linear two-port electrical systems. This feature gives the designers the ability to deal with some complex circuits as a black box placed within a larger network in a simplified manner. It also helps in partitioning large circuits into smaller ones and dealing with each one separately. Colpitts oscillator is one example of these two-port networks. It can be categorized in four categories: common A, common B, common C, and modified common C.
|

|
|

|
|

|

|
|
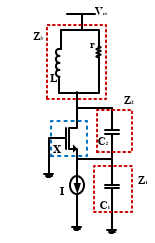
Colpitts Oscillator based on two port network
|
| |
|
|
|
Fractional-order filters based on two port networks can be classified according to the number of external impedances. The general transfer function and the important critical frequencies are deduced in terms of the transmission matrix parameters of a general two-port network for each topology. The two-port network concept and the fractional order parameters increase the design’s freedom and flexibility.